World Bank

| SECTOR | Supranational |
| RATINGS | AAA/Aaa |
| RATING OUTLOOK | Both stable |
| PAID-IN CAPITAL (30 Jun 2021) | US$19BN |
| CALLABLE CAPITAL (30 Jun 2021) | US$279BN |
|
FUNDING VOLUME FY21/FY22 |
US$67.5BN/US$55-65BN |
| RISK WEIGHT, LCR LEVEL, SOLVENCY II | 0%, Level 1, 0% |
| REPO ELIGIBILITY* | RBA, RBNZ, ECB, BoE, BoC, US Fed discount window |
*Certain requirements must be met for eligibility, for example, currency and clearing. IBRD USD benchmarks are also eligible for collateral with CME and LCH.
About World Bank
The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) was established in 1944 and is the original member of the World Bank Group. The World Bank Group consists of five organisations: IBRD, International Development Association, International Finance Corporation, Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency and International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes. At the heart of the World Bank Group’s strategy are the twin goals to end extreme poverty and promote shared prosperity.
IBRD is an international organisation and global development institution owned by 189 member countries. It supports the mission of the World Bank Group by providing loans, guarantees, risk-management products and advisory services to middle-income and creditworthy low-income countries.
IBRD, known also as World Bank in the international capital markets, has been issuing bonds to fund its sustainable-development activities and achieve a positive impact for more than 70 years.
SUSTAINABILITY OBJECTIVES OF GSS BOND PROGRAMMES
Sustainable Development Bond Program: supports sustainable development projects and programmes in member countries across 11 sectors.
Green Bond Program: supports the transition to low-carbon and climate-resilient development and growth in World Bank client countries.
| GSS BOND PROGRAMME NAMES | World Bank Sustainable Development Bond Program, World Bank Green Bond Program |
|
REFERENCE TAXONOMIES FOR THE USE OF PROCEEDS |
Green Bond Implementation Guidelines (Framework Document), Sustainable Development Bond Framework |
| FRAMEWORKS WITH WHICH THE GSS BOND PROGRAMMES ARE ALIGNED | Green Bond Principles, Sustainability Bond Guidelines |
| EXTERNAL REVIEW PROVIDERS | CICERO Shades of Green |
Sustainable funding strategy
World Bank (IBRD) issues bonds with two types of labels and has published a framework for each: World Bank Sustainable Development Bonds and World Bank Green Bonds, whereby green bonds are a subset of Sustainable Development Bonds. IBRD’s Sustainable Development Bonds align to the Sustainability Bond Guidelines, while IBRD Green Bonds align to the Green Bond Principles, each coordinated by ICMA.
All World Bank development operations are designed to achieve positive environmental and social impacts and outcomes consistent with the World Bank Group’s twin goals of ending extreme poverty and promoting shared prosperity.
All projects and programmes are approved by the World Bank board of executive directors after an extensive internal review process, which integrates sustainability policies and environmental and social requirements, and supports countries in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
World Bank takes a portfolio approach to issuing green and sustainable development bonds, which means it supports a variety of sustainable development sectors and the range of SDGs. Therefore, it does not earmark bond proceeds for individual sectors or projects within its Green Bond or Sustainable Development Bond labelled issuances.
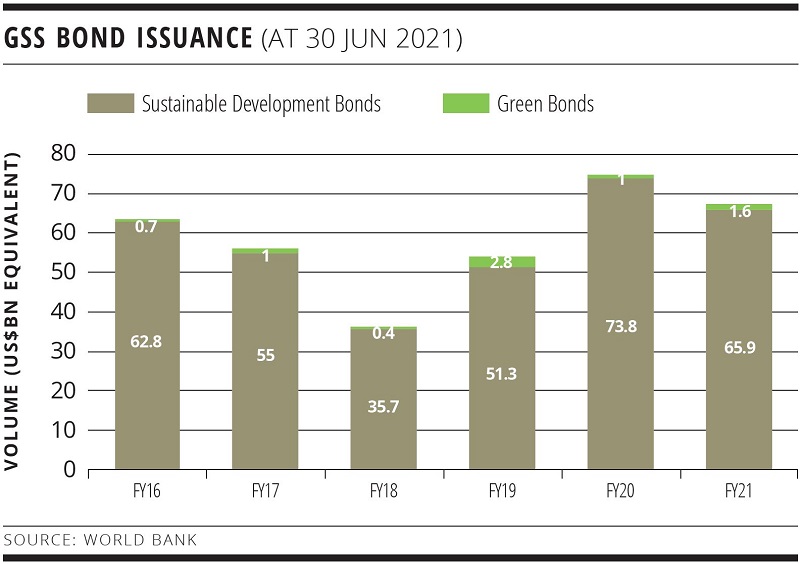
The Green Bond Program supports the financing of projects and programmes that contribute to the transition to low-carbon and climate-resilient development and growth in client countries. This includes mitigation of and adaptation to climate change – all while observing World Bank’s safeguard policies for environmental and social issues. Since 2008, World Bank has issued approximately US$16 billion equivalent in green bonds through 185 transactions in 23 currencies, as of 30 June 2021.
Sustainable Development Bonds support the financing of environmentally and socially sustainable projects and programmes in line with the organisation’s development mandate and the SDGs across 11 sectors: agriculture, fishing and forestry, education, energy and extractives, the financial sector, health, industry, trade and services, information and communications, public administration, social protection, transportation, and water, sanitation and waste management.
World Bank issues approximately US$55-65 billion equivalent annually to support these sustainable-development activities in a range of currencies and through hundreds of individual transactions.
FOR FURTHER INFORMATION PLEASE CONTACT:
World Bank Treasury
Capital Markets and Investments
+1 202 477 2880
This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
www.worldbank.org/debtsecurities

SSA Yearbook 2023
The annual guide to the world's most significant supranational, sovereign and agency sector issuers.







